Docker Mastery
By reading these notes, you will gain knowledge tailored to your role, whether you are a beginner or practitioner focusing on technical foundations or a manager looking to master Docker and Containerization Technology.
Note – This page contains a complete summary of the topics. To learn more about each topic, click on the (
Expand), Topic-Heading, Image, or ‘Click Here’ hyperlink.
Before reading this document, please read DevOps Essentials and DevSecOps Essentials
—
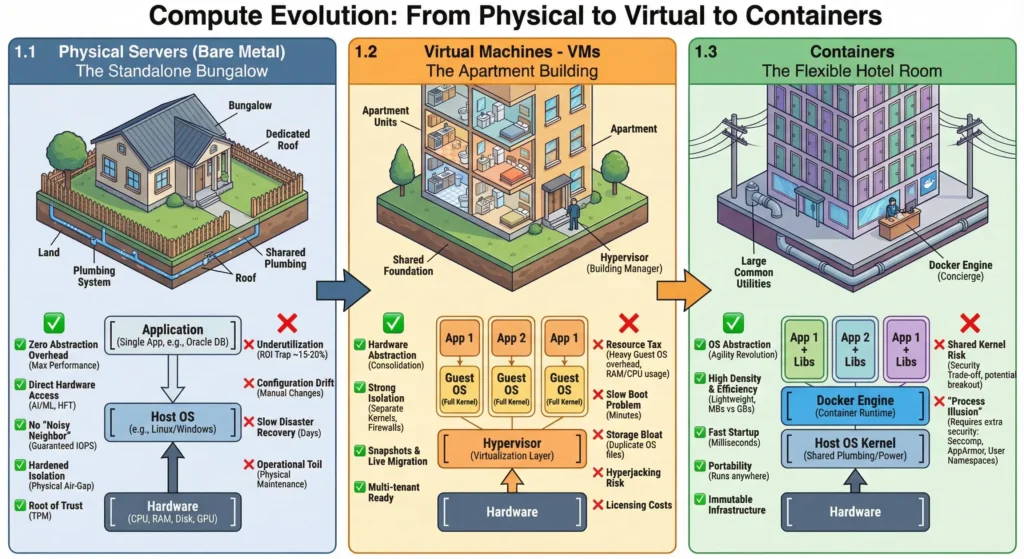
1. Evolution
| Topic | Short Note |
| Bare Metal | Provides physical air-gap but suffers from low utilization (15-20%) and configuration drift. |
| Virtual Machines | Slices hardware into “Apartments” but incurs a heavy “Resource Tax” (~500MB RAM/kernel). |
| Containers | Shares Host Kernel. Lightweight (starts in ms), high density, but carries kernel breakout risks. |
—
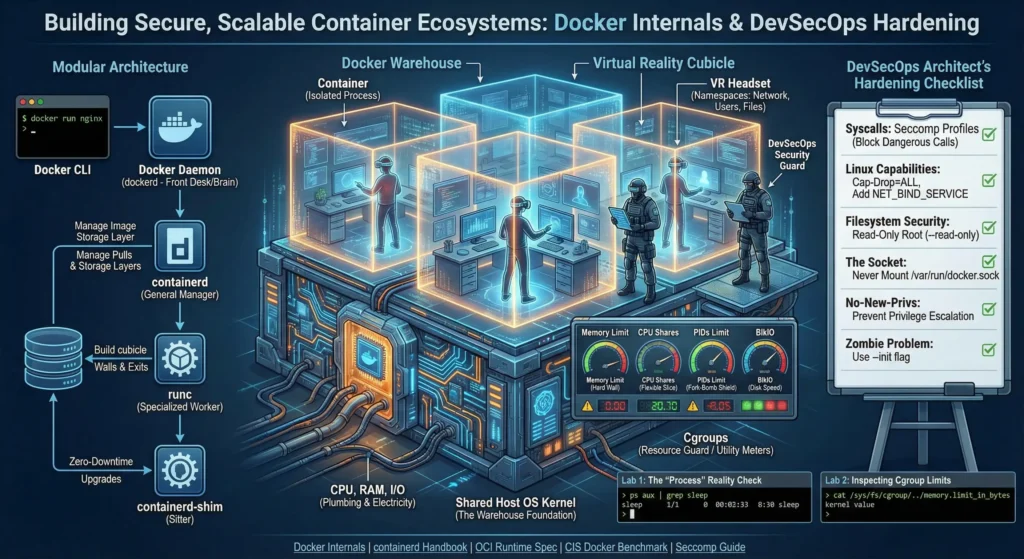
2. Internals
| Topic | Short Note |
| Shared Kernel | Incredibly fast but requires Hardened Kernels or Minimal OS to mitigate panic/breakout. |
| Namespaces | Provides Logical Isolation (PID, NET, MNT, USER) so processes feel alone; not physical isolation. |
| Cgroups | Limits CPU/RAM to prevent “Noisy Neighbors” and uses PID limits to stop Fork Bombs. |
| Modular Runtime | Modern OCI-compliant stack. The Shim process allows Zero-Downtime daemon upgrades. |
—
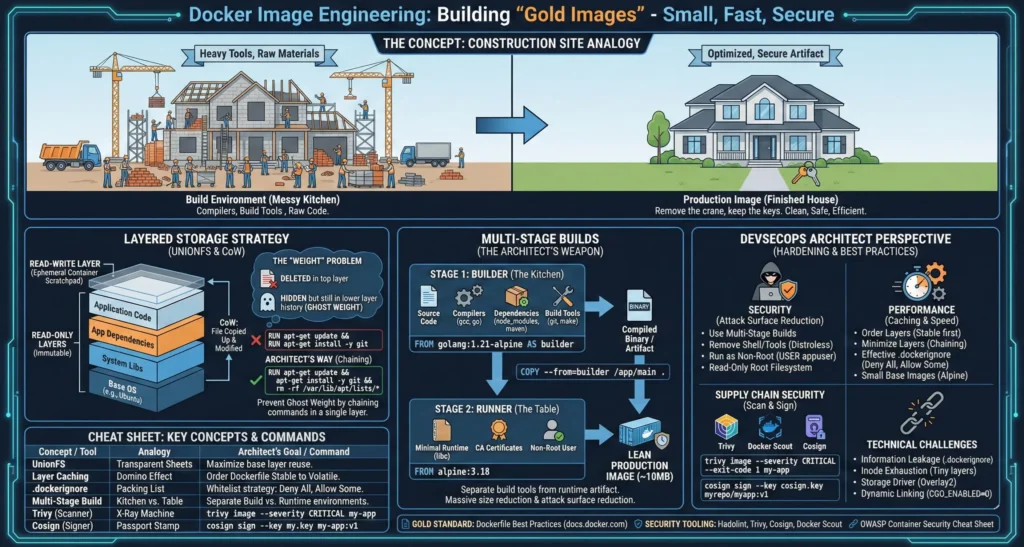
3. Images
| Topic | Short Note |
| Layering & CoW | Uses Copy-on-Write. Chain commands (&&) in Dockerfile to prevent “Ghost Weight” bloat. |
| Multi-Stage Builds | Architect’s Weapon. Separates heavy SDKs from final binary (e.g., 800MB → 15MB). |
| .dockerignore | Mandatory to prevent leaking secrets (like .env) and to speed up build context transfer. |
—
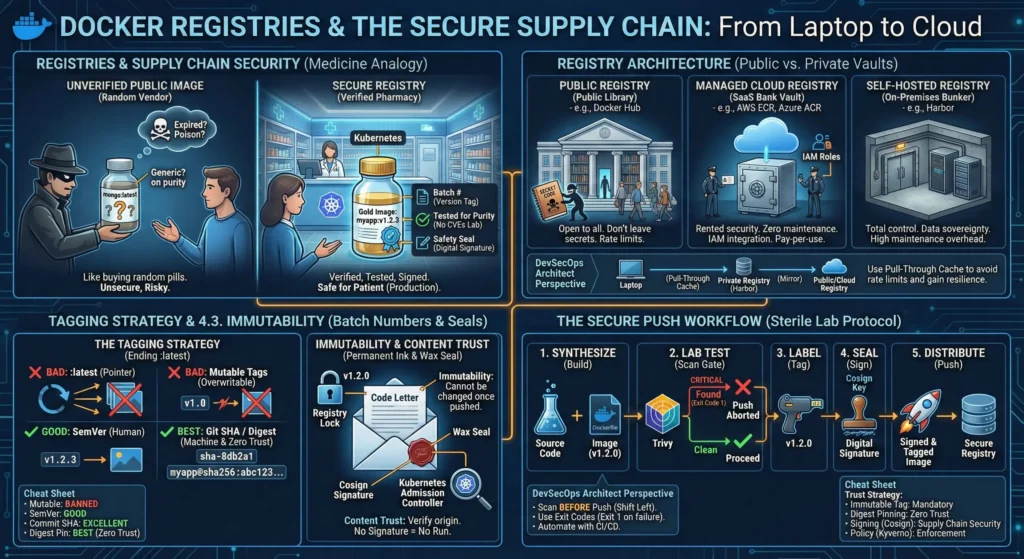
4. Registries
| Topic | Short Note |
| Supply Chain | Use Private Registries (ECR/Harbor) with Vulnerability Scanning & Retention Policies enabled. |
| Tagging Strategy | Never use :latest. Use Semantic Versioning and Git SHA. Enforce Tag Immutability. |
| Content Trust | Move from trusting tags to trusting signatures (Cosign/Sigstore). Block unsigned images. |
—
5. Compose
| Topic | Short Note |
| Infra as Code | Declarative YAML ensures environment parity. Defines Services, Networks, and Volumes in code. |
| Service Discovery | Embedded DNS (127.0.0.11) allows containers to resolve names (e.g., db) automatically. |
| Healthchecks | Prevents Race Conditions. APIs wait for the DB to be service_healthy before starting. |
| Profiles & Overrides | Use --profile for selective startups (e.g., monitoring stack) and override.yml for per-environment config patching. |
—
6. Networking
| Topic | Short Note |
| Bridge | Default isolation. Use User-Defined Bridges for automatic DNS and “DMZ” segmentation. |
| Host | Removes isolation. Security Nightmare; use only for system monitoring tools. |
| Overlay | Backbone of Swarm/K8s. Always enable Data Plane Encryption (--opt encrypted) for safety. |
| Macvlan/IPvlan | Assigns physical network IPs to containers. Use for legacy app migration or monitoring. |
—
7. Storage
| Topic | Short Note |
| Writable Layer | Temporary UnionFS storage. Slow due to CoW; data is lost on delete. Never use for Prod data. |
| Volumes | Stored in /var/lib/docker/volumes/. High perf, secure, persists data. |
| Bind Mounts | Maps host folders. Great for Hot Reloading code, but risky (Host Escape) in production. |
| tmpfs | RAM-only storage. Ultimate Anti-Forensics tool for secrets/tokens; data wipes on stop. |
| Storage Drivers | Overlay2 is standard. Bypass drivers using Volumes for high-IOPS workloads (Databases). |
—
8. Observability
| Topic | Short Note |
| Logs | Avoid default json-file bloat. Enforce Log Rotation and stream to central vaults (Loki). |
| Metrics | Use cAdvisor (sidecar) to feed container stats into Prometheus/Grafana for alerting. |
| Distributed Tracing | “The Request GPS.” Use OpenTelemetry to track requests as they jump between microservices. |
—
9. Hardening
| Topic | Short Note |
| Rootless Mode | Run the Daemon as a non-root user. Mitigates 90% of container breakout attacks. |
| Seccomp & AppArmor | “The Invisible Shield.” Restrict syscalls (like mount or ptrace) to reduce the attack surface. |
| CIS Benchmarks | The “Audit Checklist.” Use tools like Docker Bench for Security to validate host configuration. |